nTopology 5.0.4 Win x64
Free Download nTopology 5.0.4 | 1.7 Gb
nTopologyis pleased to announce the availability ofnTopology 5.0.4. This major release includes our new implicit modeling kernel, parallel surface remeshing, and the ability to import implicit body features. This release also refreshes the viewport with CAD color import, customizable glyph colors, and right-click menus.
Owner:nTopology
Product Name:nTopology
Version:5.0.4
Supported Architectures:x64
Website Home Page :www.ntop.com
Languages Supported:english
System Requirements:Windows *
Size:1.7 Gb
Implicit Modelling Kernel
- We updated the implicit kernel to perform implicit and field calculations in nTop with increased precision. For more information on this update and recommended actions, please refer to the New Implicit Modeling Kernel and Outline of expected differences articles on our support landing page.
Boolean Union and Boolean Subtract
- The Boolean Union and Boolean Subtract blocks now run faster on large lists of primitive shapes, with up to 100x performance improvements and up to 1000x improvement for lists of 10,000 to 100,000 items and more. This includes downstream operations such as meshing and slicing.
- When the Blend type input is set to "Sharp" (fastest), "Rounded", or "Chamfered", and the list of inputs contains primitive shapes (sphere, cylinder, cone, box, skewed box, point, torus), the Boolean block will run faster.
Import Implicit Body
- The Import Implicit Body block imports a *.implicit file from a designated path.
- Common uses:
. Import an Implicit Body saved from any nTop workflow to use in your current workflow.
. Validate/Inspect the file before sending it to an implicit interop partner.
. Share an Implicit Body designed in nTop, removing your IP-containing nTop notebooks.
- Block Name: Import Implicit Body
- Location: Utilities > Exchange
. Path: The input file path.

Close
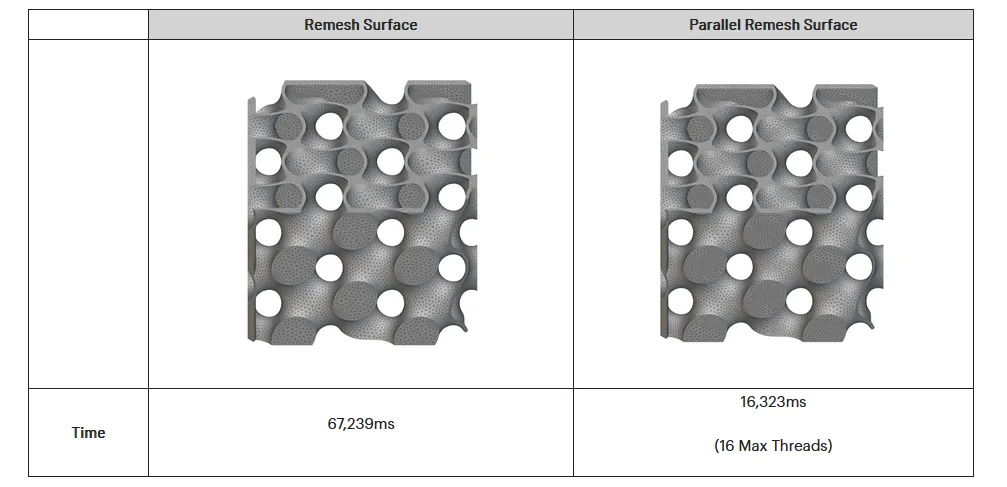
Parallel Remesh Surface
- The Parallel Remesh Surface block re-meshes an existing surface mesh using parallel processing.
- The algorithm automatically partitions the input mesh and pre-meshes each partition in parallel.
- The number of partitions is equal to the Max Threads input.
- Block Name: Parallel Remesh Surface
- Location: Beta > Simulation
- Surface: Surface mesh to remesh.
. Edge Length: The target edge length of the generated elements.
. Shape: The element shape of the output mesh.
. Span Angle: The maximum spanning angles for elements generated on curved surfaces.
. Growth Rate: The rate at which the size of adjacent elements can grow.
. Feature Angle: The maximum angle used to compute the preserved edges in the input surface automatically.
. Min Edge Length: The minimum allowed edge length of the generated elements in the output mesh.
. Chord Height: The maximum distance from the midpoint of an element edge to the input surface.
. Min Feature Size: The minimum small feature size to control the deletion of small features.
. Max Threads: The number of parallel threads the meshing algorithm uses. If not provided, the Max Threads will be set to the maximum available on the machine up to 32.
. Output: Mesh
Close
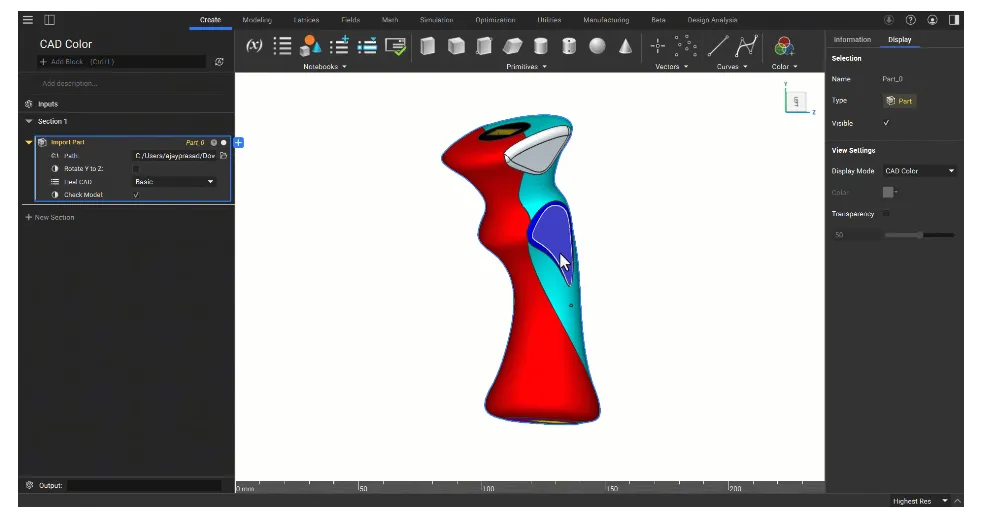
CAD Color
- We've added a display mode for viewing the colors of imported CAD geometry. You can still change it to a custom color by switching Display Mode to "Default Color."
Close
View Setting Improvements
- We've added a Visibility checkbox to the right-side panel so you can quickly see if the selected object is visible and change its visibility near the other view settings.
- The FE Cylindrical Restraint type now has an option in the right-side panel to turn the visibility of the axis on and off. The axis will be on by default.
- You can now change the color of simulation glyphs with a "Custom Color" Display Mode and return to the "Default Color" Display Mode.
- We've moved the view settings for Unit Cells and Cell Maps from the HUD to the right-side panel for ease of use.
- If you change any display settings and save your file, the settings will be saved when you reopen the file.

Close
Right Click Menus in the Viewport
- You can now use right-click menus in the viewport to perform convenient actions on selected objects, including Isolate, Visibility, Transparency, Field Viewer, Section Cut, Zoom to Fit, and Precise Render.
- You can also click in the empty space in the viewport for general actions, including Field Viewer, Section Cut, Zoom to Fit, Capture Image, access Named views, Select All Visible, Show Grid, and Show Ruler.
- Existing viewport right-click menus specific to CAD and Meshes are still available at the top of the right-click menu.
JSON from Dictionary
- The JSON from Dictionary block converts a Dictionaryinput into a JSON format.
- JSON files can now be created and exported from data within nTop using the Export JSON block, which is used upstream.
- Block Name: JSON from Dictionary
- Location: Beta > Create
- Dictionary: Text-based Dictionary to convert into a JSON format.
- Output: JSON
Export JSON
- Export a JSON file.
- Combining this block and JSON from the Dictionary block enables exporting information in JSON format.
- Block Name: Export JSON
- Location: Beta > Create
- File Path: System path of exported JSON file.
- JSON: JSON to export
- Output: JSON File Data

Close
Usage Improvements
- We have updated the Import CFD Analysis Result and Import Static Structural Result blocks to support importing *.vtk files.
- We've updated the selection color in the viewport to the same blue as the selection color in the notebook and outline for visual continuity.

Close
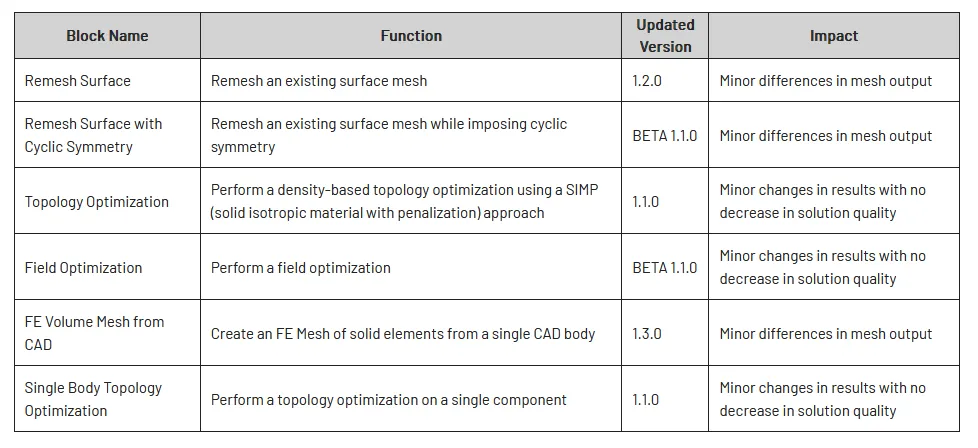
Block Updates
- We updated the six native and eight toolkit blocks related to meshing and simulation due to a meshing library update. The previous versions of these blocks have been deprecated and removed from the software. The blocks, their function, the updated version, and the performance difference from the previous version are outlined in the following table:
Close
- We have updated the Topology Optimization and Field Optimization blocks to include improved error messaging and have added a new optional Move Limit input for the Topology Optimization block.
. The new Move Limit input adds an upper bound on how large a step in the optimization problem can be at each iteration. This can be used to help control the convergence for complicated topology optimizations.
. When this input is left blank, the current heuristic, which depends on the chosen responses and constraints, will continue to be used.
- The Field from Point Map block has been updated to simplify the "Interpolation" and "Extrapolation" options into one single "Interpolation" input. To match the previous behavior of "Extrapolation: None," which produced a constant field of zero outside the part's convex hull, the If-Else block can be used along with the "Body" property of Delaunay Volume Mesh.
- The Radial Basis Field from Point Map block has been updated to simplify the "Factor" and "Extrapolation" options into one single "Factor" input. To match the previous behavior of "Extrapolation: None", which produced a constant field of zero outside the convex hull of the part, the If-Else block can be used along with the "Body" property of Delaunay Volume Mesh.
- The Export Implicit Body block and nTop Plugin for EOSPRINT have been moved from Beta to Production.
nTopologyintroduced the concept of implicit modeling for mechanical design, which is an innovative, modern, and scalable way define parts and products. It has many benefits to end-users and companies, such as the elimination of model failures, speed of changes or iterations, and scalability to name a few. But implicit modeling enables so much more. In this informational session, we'll explore a topic that is redefining product development - field-driven design. In short, field-driven design is a way for design, analysis, and manufacturing teams to overlay information into one engineering model. This approach enables orders of magnitude increase in design iteration speed and greatly improves collaboration between teams.
How Field-Driven Design Allows Engineers to Design for Additive Manufacturing
Watch this information session where we'll define field-driven design, show examples of how it enables better knowledge sharing, and show how it promotes the development of more sophisticated, highly engineered products. You'll also better understand how nTopology is addressing today's engineering problems through its nTop Platform product.
nTopologywas founded in 2015 to enable engineers and designers to create any geometry - no matter how complex - and meet the requirements of high-performance products.
Links are Interchangeable - No Password - Single Extraction
